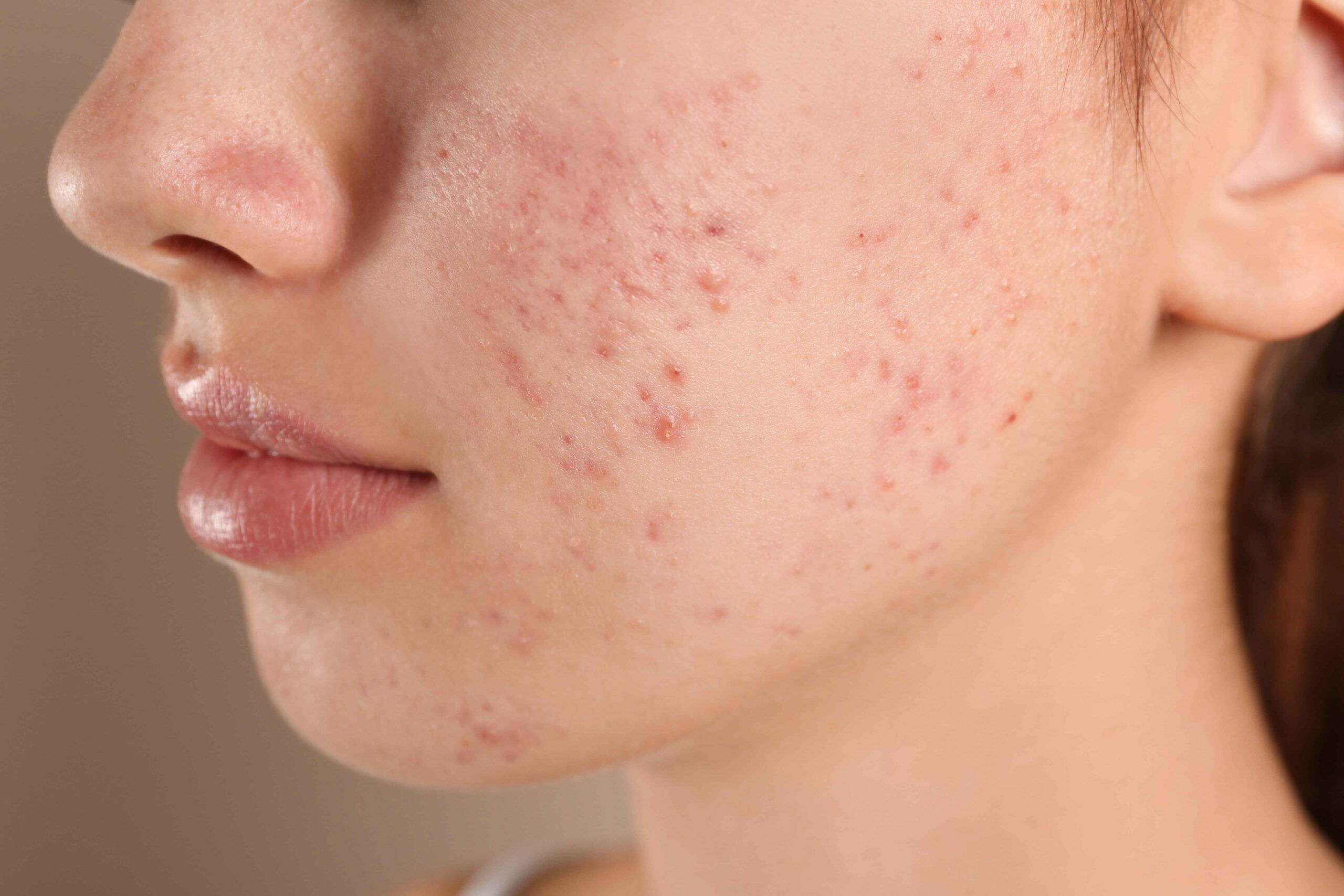
Acne is a common skin condition that happens when hair follicles under the skin plug with Sebum and dead skin cells, becoming clogged. Sebum—oil that helps keep skin from drying out—and dead skin cells plug the pores, which leads to outbreaks of lesions, commonly called pimples or zits.
Three Types of Acne
- Comedonal – Comedones are small, flesh-colored, white, or dark bumps that give skin a rough texture. The bumps are caused by acne. Blackheads are open comedones, and Whiteheads are closed comedones.
- Papules and pustules – What’s the difference between a papule and a pustule? Acne papules are solid, inflamed bumps in your skin that don’t have a white or yellow pus-filled tip. Pustules have a white or yellow pus-filled tip. Papules can develop into pustules.
- Nodulocystic – Nodular or Cystic acne is a type of inflammatory, painful acne that requires treatment from a healthcare provider or Dermatologist. Prescription oral medications and topical creams may be needed.
Four Main Factors Cause Acne
- Excess oil (sebum) production
- Hair follicles clogged by oil & dead skin cells
- Bacteria
- Inflammation
Acne Scars
Acne Scarring is the result of inflammation of acne. The acne pore swells, and a breakdown occurs in the wall of the pore.
Milia
Milia or “milk spots” are small, white cysts on your skin. Cysts are filled pockets under the surface of your skin. Milia are harmless and only affect your appearance. It’s common to confuse the white bumps on your face with whiteheads, a type of acne.
Scar Removal
A scar is the body’s natural way of healing and replacing lost or damaged skin. A growth of tissue marking the spot where the skin has healed after an injury. A scar is usually composed of fibrous tissue. Scars may be formed for many different reasons, including as a result of infections, surgery, injuries, or inflammation of the tissue.
Types of Scars
- Normal fine-line scars
- Keloid scars
- Hypertrophic scars
- Pitted or Sunken scars
- Scar Contractures
Normal Fine-Line Scars
A minor wound like a cut will usually heal to leave a raised line, gradually fading and flattening over time.
This process can take up to 2 years. The scar will not disappear completely, leaving you with a visible mark or line.
Fine-line scars are common following a wound or after surgery. They are not usually painful but may be itchy for a few months. The scar tissue may fade on darker skin types to leave a brown or white mark.
Keloid Scars
A keloid scar is an overgrowth of tissue that happens when too much collagen is produced at the site of a wound. The scar keeps growing, even after the wound has healed.
Keloid scars are raised above the skin and can be pink, red, the same color, or darker than the surrounding skin. They’re often itchy or painful and can restrict movement if tight and near a joint.
You might get them in multiple places if you’re prone to developing keloids. A keloid scar isn’t harmful to your physical health but can cause emotional distress.
Hypertrophic Scars
Like keloid scars, hypertrophic scars result from excess collagen produced at a wound’s site. A hypertrophic scar is a thick, raised scar that’s an abnormal response to wound healing.
Unlike keloid scars, hypertrophic scars do not extend beyond the boundary of the original wound. They may continue to thicken for up to 6 months before gradually improving over a few years. They commonly occur in taut skin areas following skin trauma, burns, or surgical incisions.
Pitted or Sunken Scars
Some scars caused by skin conditions, such as acne and chickenpox, can appear sunken or pitted. Pitted scars, also known as atrophic or “ice-pick” scars, can also develop due to an injury that causes a loss of underlying fat.
An atrophic scar is an indented scar that heals below the normal layer of skin tissue. Atrophic scars form when the skin is unable to regenerate tissue. As a result, it leaves behind imbalanced scarring. Atrophic scars are often the result of severe acne or chickenpox.
Scar Contractures
Burns often cause scar contractures. They happen when the skin “shrinks,” leading to tightness and a restriction in movement.
A scar contracture results from a contractile wound-healing process occurring in a scar that has already been re-epithelialized and adequately healed.